‘F Aeolian’ is the 6th mode of the A flat major scale. The notes in F Aeolian are:
F – G – Ab – Bb – C – Db – Eb
If you have read the post on understanding the aeolian mode, you will know that the aeolian mode contains a ‘flat 3’, a ‘flat 6’ and a ‘flat 7’ (parallel approach). You will also know that it is the 6th mode of the major scale (derivative approach). The aeolian mode is a very commonly used mode and is also known as the ‘natural minor scale’. Let’s briefly look at how to construct F aeolian using both the parallel approach and the derivative approach.
F Aeolian Mode Using The Parallel Approach
F Major has the following notes:
F – G – A – Bb – C – D – E
If we ‘lower’ the 3rd note (A), 6th note (D) and 7th note (E), we get the following:
F – G – Ab – Bb – C – Db – Eb
F Aeolian Mode Using The Derivative Approach
F is the 6th note of the Ab major scale:
Ab – Bb – C – Db – Eb – F – G
If we play the Ab major scale and start on the 6th note we get the following:
F – G – Ab – Bb – C – Db – Eb
Let’s look at the F aeolian mode in the different positions on the guitar fretboard:
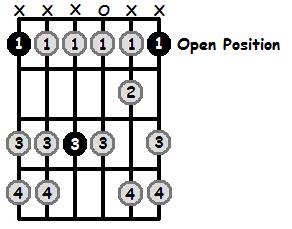
F Aeolian in the Open Position
Firstly, let’s look at the open position:

F Aeolian CAGED Positions
Now let’s look at F aeolian in the 5 different CAGED positions along the fretboard.
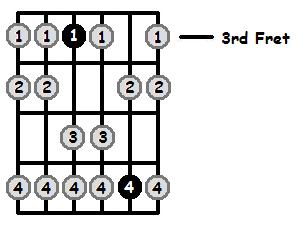
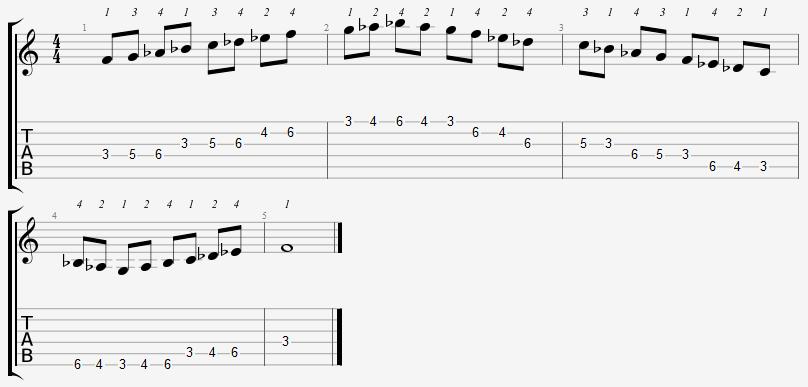
F Aeolian 3rd Position (Lowest Fret is 3)
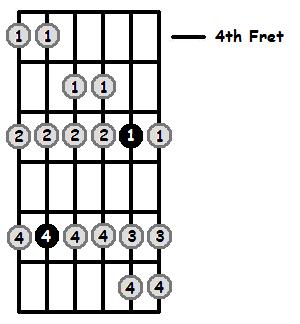
F Aeolian 4th Position (Lowest Fret is 4)

F Aeolian 8th Position (Lowest Fret is 8)
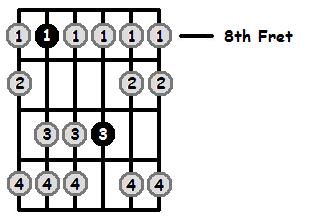

F Aeolian 9th Position (Lowest Fret is 9)


F Aeolian 12th Position (Lowest Fret is 12)
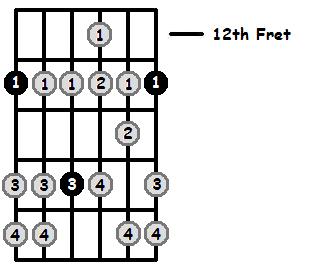

That covers the 5 basic positions and the open position of F aeolian along the guitar fretboard. For an in depth explanation of the aeolian mode, check out aeolian mode explained.
Further Reading
- Fm chord (F Aeolian works well over this chord)
- Fm7 chord (F Aeolian works well over this chord)
- Ab Major scale is the relative Major of F minor
